Load the geometrical object from a binary 2D image
In this example, we will:
- Read a 2D binary image from a binary file (for a 3D image volume see Images 3D)
- Build a 2D cartesian OpenFPM grid with same dimensions as the image (1 particle for each pixel in x and y) or refined by arbitrary factor in dimension of choice (e.g. to get a isotropic grid)
- Assign pixel value to a grid node property
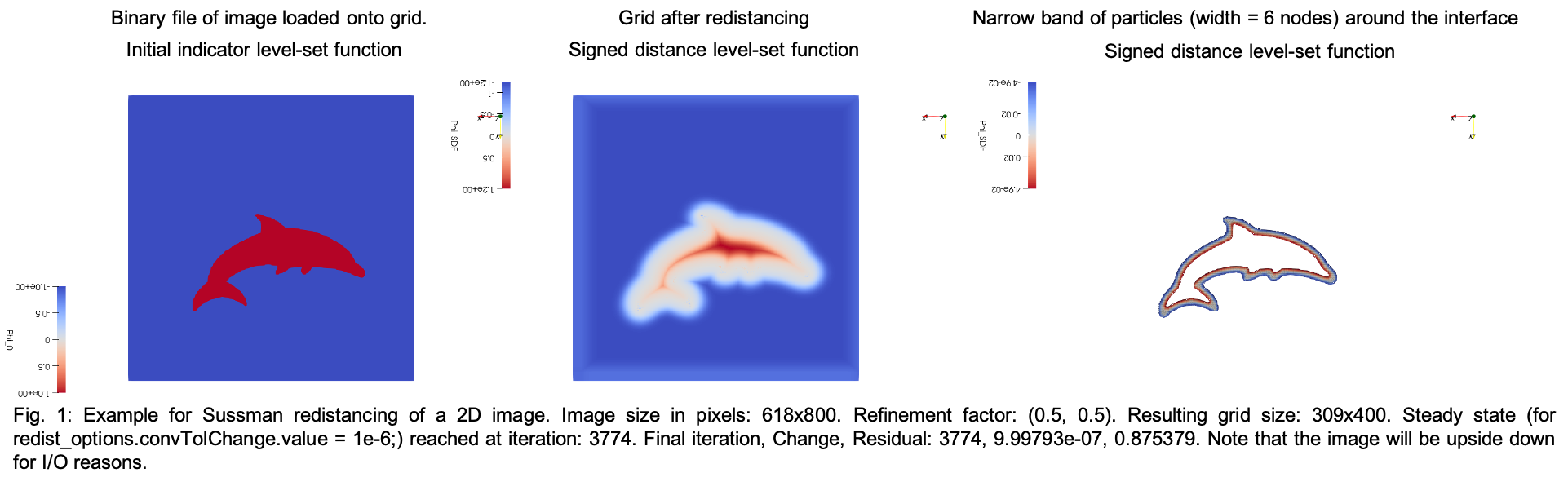
- Run the Sussman Redistancing and get the narrow band around the interface (see also: Disk 2D and example_sussman_sphere)
Output: print on promt : Iteration, Change, Residual (see: DistFromSol::change, DistFromSol::residual) writes vtk and hdf5 files of: 1.) 2D grid with geometrical object pre-redistancing and post-redistancing (Phi_0 and Phi_SDF, respectively) 2.) particles on narrow band around interface.
Visualization of example output in Paraview
Include
These are the header files that we need to include:
Header file containing functions for loading pixel values from 2D image or 3D image stack (volume) st...
Class for getting the narrow band around the interface.
Header file containing functions for creating files and folders.
Class for reinitializing a level-set function into a signed distance function using Sussman redistanc...
Initialization, indices and output folder
Again we start with
- Initializing OpenFPM
- Setting the output path and creating an output folder This time, we also set the input path and name of the binary image that we want to load onto the grid. For this example we provide 3 simple example images. The original (e.g. tiff) image has been converted into -1 / +1 values. A jupyter notebook that does this can be found here:
image2binary_dolphin.ipynb.
Optionally, we can define the grid dimensionality and some indices for better code readability later on.
x: First dimensiony: Second dimensionPhi_0_grid: Index of property that stores the initial level-set-functionPhi_SDF_grid: Index of property where the redistancing result should be written to
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
std::string image_name = "dolphin";
typedef double phi_type;
openfpm_init(&argc, &argv);
const std::string path_output = cwd + "/output_" + image_name;
const std::string path_input ="input/";
const std::string path_to_image = path_input + image_name + ".bin";
const std::string path_to_size = path_input + "size_" + image_name + ".csv";
const unsigned int grid_dim = 2;
const size_t x = 0;
const size_t y = 1;
const size_t Phi_0_grid = 0;
const size_t Phi_SDF_grid = 1;
const size_t Phi_SDF_vd = 0;
const size_t Phi_grad_vd = 1;
const size_t Phi_magnOfGrad_vd = 2;
static void create_directory_if_not_exist(std::string path, bool silent=0)
Creates a directory if not already existent.
static std::string get_cwd()
Gets the current working directory and returns path as string.
Set refinement factor
If we want that the grid has a different resolution as the image, we can set a refinement factor. In the refinement array, we define by which factor the grid resolution should be changed w.r.t. the image resolution. This can be useful for example when you want to have an isotropic grid but the underlying image is anisotropic (as it often happens for microcsopic z-stacks rather than 2D images).
const phi_type refinement [] = {0.5, 0.5};
Get size from image_size.csv
Here we read the image size (number of pixel values per dimension) from a csv file. Alternatively, you can directly define the image size as: std::vector<size_t> stack_size {#pixels in x, #pixels in y}. We use this image size and the refinement factor to set the grid size sz.
std::vector<int> stack_size =
get_size(path_to_size);
auto & v_cl = create_vcluster();
if (v_cl.rank() == 0)
{
for(std::vector<int>::size_type i = 0; i != stack_size.size(); i++)
{
std::cout << "#Pixel in dimension " << i << " = " << stack_size[i] << std::endl;
std::cout << "original refinement in dimension " << i << " = " << refinement[i] << std::endl;
}
}
const size_t sz[grid_dim] = {(size_t)std::round(stack_size[x] * refinement[x]), (size_t)std::round(stack_size[y] *
refinement[y])};
std::vector< int > get_size(const std::string &path_to_file)
Read the number of pixels per dimension from a csv-file in order to create a grid with the same size.
Run Sussman redistancing and get narrow band
Once we have loaded the geometrical object from the 2D image onto the grid, we can perform Sussman redistancing and get the narrow band the same way as it is explained in detail here: Disk 2D and here: Sphere 3D.
grid_in_type g_dist(sz, box, ghost);
g_dist.setPropNames({"Phi_0", "Phi_SDF"});
init_grid_and_ghost<Phi_0_grid>(g_dist, -1.0);
load_pixel_onto_grid<Phi_0_grid>(g_dist, path_to_image, stack_size);
g_dist.write(path_output + "/grid_from_images_initial", FORMAT_BINARY);
redist_options.min_iter = 1e3;
redist_options.max_iter = 1e4;
redist_options.convTolChange.value = 1e-7;
redist_options.convTolChange.check = true;
redist_options.convTolResidual.value = 1e-6;
redist_options.convTolResidual.check = false;
redist_options.interval_check_convergence = 1e3;
redist_options.width_NB_in_grid_points = 10;
redist_options.print_current_iterChangeResidual = true;
redist_options.print_steadyState_iter = true;
redist_options.save_temp_grid = true;
redist_obj.run_redistancing<Phi_0_grid, Phi_SDF_grid>();
g_dist.write(path_output + "/grid_images_post_redistancing", FORMAT_BINARY);
size_t bc[grid_dim] = {NON_PERIODIC, NON_PERIODIC};
vd_type vd_narrow_band(0, box, bc, ghost_vd);
vd_narrow_band.setPropNames({"Phi_SDF", "Phi_grad", "Phi_magnOfGrad"});
narrowBand.get_narrow_band<Phi_SDF_grid, Phi_SDF_vd, Phi_grad_vd, Phi_magnOfGrad_vd>(g_dist, vd_narrow_band);
vd_narrow_band.write(path_output + "/vd_narrow_band_images", FORMAT_BINARY);
openfpm_finalize();
return 0;
}
This class represent an N-dimensional box.
Class for getting the narrow band around the interface.
Class for reinitializing a level-set function into a signed distance function using Sussman redistanc...
This is a distributed grid.
Structure to bundle options for redistancing.
aggregate of properties, from a list of object if create a struct that follow the OPENFPM native stru...
Full code
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
std::string image_name = "dolphin";
typedef double phi_type;
openfpm_init(&argc, &argv);
const std::string path_output = cwd + "/output_" + image_name;
const std::string path_input ="input/";
const std::string path_to_image = path_input + image_name + ".bin";
const std::string path_to_size = path_input + "size_" + image_name + ".csv";
const unsigned int grid_dim = 2;
const size_t x = 0;
const size_t y = 1;
const size_t Phi_0_grid = 0;
const size_t Phi_SDF_grid = 1;
const size_t Phi_SDF_vd = 0;
const size_t Phi_grad_vd = 1;
const size_t Phi_magnOfGrad_vd = 2;
const phi_type refinement [] = {0.5, 0.5};
std::vector<int> stack_size =
get_size(path_to_size);
auto & v_cl = create_vcluster();
if (v_cl.rank() == 0)
{
for(std::vector<int>::size_type i = 0; i != stack_size.size(); i++)
{
std::cout << "#Pixel in dimension " << i << " = " << stack_size[i] << std::endl;
std::cout << "original refinement in dimension " << i << " = " << refinement[i] << std::endl;
}
}
const size_t sz[grid_dim] = {(size_t)std::round(stack_size[x] * refinement[x]), (size_t)std::round(stack_size[y] *
refinement[y])};
grid_in_type g_dist(sz, box, ghost);
g_dist.setPropNames({"Phi_0", "Phi_SDF"});
init_grid_and_ghost<Phi_0_grid>(g_dist, -1.0);
load_pixel_onto_grid<Phi_0_grid>(g_dist, path_to_image, stack_size);
g_dist.write(path_output + "/grid_from_images_initial", FORMAT_BINARY);
redist_options.min_iter = 1e3;
redist_options.max_iter = 1e4;
redist_options.convTolChange.value = 1e-7;
redist_options.convTolChange.check = true;
redist_options.convTolResidual.value = 1e-6;
redist_options.convTolResidual.check = false;
redist_options.interval_check_convergence = 1e3;
redist_options.width_NB_in_grid_points = 10;
redist_options.print_current_iterChangeResidual = true;
redist_options.print_steadyState_iter = true;
redist_options.save_temp_grid = true;
redist_obj.run_redistancing<Phi_0_grid, Phi_SDF_grid>();
g_dist.write(path_output + "/grid_images_post_redistancing", FORMAT_BINARY);
size_t bc[grid_dim] = {NON_PERIODIC, NON_PERIODIC};
vd_type vd_narrow_band(0, box, bc, ghost_vd);
vd_narrow_band.setPropNames({"Phi_SDF", "Phi_grad", "Phi_magnOfGrad"});
narrowBand.get_narrow_band<Phi_SDF_grid, Phi_SDF_vd, Phi_grad_vd, Phi_magnOfGrad_vd>(g_dist, vd_narrow_band);
vd_narrow_band.write(path_output + "/vd_narrow_band_images", FORMAT_BINARY);
openfpm_finalize();
return 0;
}
