Solving a gray scott-system in 3D
This example is just an improved version of the previous 3D Gray scott example. It can use VCDevel library for vectorization in C++ or Fortran multi-array code update. For the first case the library VCDevel must be installed. It can be installed using the command ./script/install_VCDEVEL.sh /where/are/the/dependencies/directory and changing the Makefile to include the VCDevel library like show in the Makefile. By default this example use fortran update because does not require external libraries. In particular we do the following improvements we separate U and V in two grids in order to vectorize. Every loop now handle 4 double in case of AVX-256 and 2 double in case of SSE. We also avoid to use the function copy and we alternate the use of the fields New and Old. If at the first iteration we read from Old and we write on New in the second iteration we read from New and we write on Old. The last improvement is write on hdf5 rather that VTK. VTK writers are convenient but are slow for performances. HDF5 files can be saved with save() reload with load() and after loading can be written on VTK with write this mean that HDF5 files can be easily converted into VTK in a second moment. Not only but because HDF5 files can be saved on multiple processors and reloaded on a different number of processors, you can use this method to stitch VTK files together.
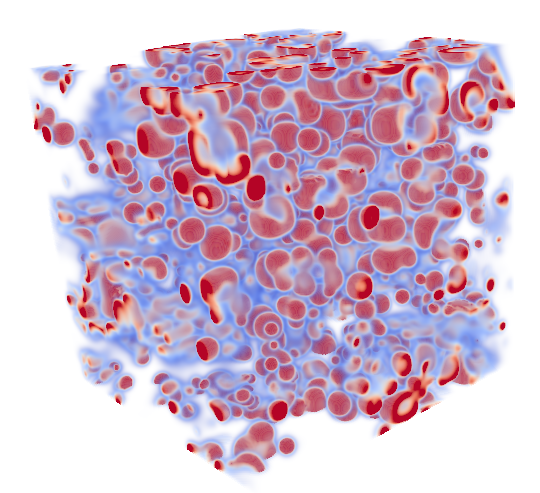
In figure is the final solution of the problem
- See also
- Solve equation
constexpr int x = 0;
constexpr int y = 1;
constexpr int z = 2;
extern "C" void update_new(const int* lo, const int* hi,
double* u, const int* ulo, const int* uhi,
double* v, const int* vlo, const int* vhi,
double* flu, const int* fulo, const int* fuhi,
double* flv, const int* fvlo, const int* fvhi,
const double * dt,
const double * uFactor,
const double * vFactor,
const double *
F,
const double * K);
[v_transform metafunction]
Here we create 2 distributed grid in 3D Old and New splitting U and V in two different fields. In particular because we want that all the grids are distributed across processors in the same way we pass the decomposition of the first grid.
double spacing[3] = {OldU.spacing(0),OldU.spacing(1),OldU.spacing(2)};
init(OldU,OldV,NewU,NewV,domain);
This is a distributed grid.
OutputIteratorT OffsetT ReductionOpT OuputT init
< [in] The initial value of the reduction
Alternate New and Old field to run one step, switch between old and new if the iteration is even or odd. The function step is nothing else than the implementation of Gray-Scott 3D in the previous example but in a more optimized way.
if (i % 2 == 0)
{
step(OldU,OldV,NewU,NewV,star_stencil_3D,uFactor,vFactor,deltaT,
F,K);
NewU.ghost_get<0>();
NewV.ghost_get<0>();
}
else
{
step(NewU,NewV,OldU,OldV,star_stencil_3D,uFactor,vFactor,deltaT,
F,K);
OldU.ghost_get<0>();
OldV.ghost_get<0>();
}
In this function we show two methods to optimize this function.
- We can use the macro WHILE_M passing the stencil definition, ITERATE_3D to define the loop, END_LOOP to close the loop, and use the function function getStencil<0>() to retrieve the stencil points. Additionaly we can use Vc::double_v instead of double to vectorize the code. This method give the advantage to keep all the code in C++.
Vc::double_v uFactor = uFactor_s;
Vc::double_v vFactor = vFactor_s;
WHILE_M(OldU,star_stencil_3D)
auto & U_old = GET_GRID_M(OldU);
auto & V_old = GET_GRID_M(OldV);
auto & U_new = GET_GRID_M(NewU);
auto & V_new = GET_GRID_M(NewV);
ITERATE_3D_M(Vc::double_v::Size)
auto Cp = it.getStencil<0>();
auto mx = it.getStencil<1>();
auto px = it.getStencil<2>();
auto my = it.getStencil<3>();
auto py = it.getStencil<4>();
auto mz = it.getStencil<5>();
auto pz = it.getStencil<6>();
Vc::double_v u_c(&U_old.get<0>(Cp),Vc::Unaligned);
Vc::double_v u_mz(&U_old.get<0>(mz),Vc::Unaligned);
Vc::double_v u_pz(&U_old.get<0>(pz),Vc::Unaligned);
Vc::double_v u_my(&U_old.get<0>(my),Vc::Unaligned);
Vc::double_v u_py(&U_old.get<0>(py),Vc::Unaligned);
Vc::double_v u_mx(&U_old.get<0>(mx),Vc::Unaligned);
Vc::double_v u_px(&U_old.get<0>(px),Vc::Unaligned);
Vc::double_v v_c(&V_old.get<0>(Cp),Vc::Unaligned);
Vc::double_v v_mz(&V_old.get<0>(mz),Vc::Unaligned);
Vc::double_v v_pz(&V_old.get<0>(pz),Vc::Unaligned);
Vc::double_v v_my(&V_old.get<0>(my),Vc::Unaligned);
Vc::double_v v_py(&V_old.get<0>(py),Vc::Unaligned);
Vc::double_v v_mx(&V_old.get<0>(mx),Vc::Unaligned);
Vc::double_v v_px(&V_old.get<0>(px),Vc::Unaligned);
Vc::double_v out1 = u_c + uFactor * (u_mz + u_pz +
u_my + u_py +
u_mx + u_px +
- 6.0 * u_c) +
- deltaT * u_c * v_c * v_c
- deltaT *
F * (u_c - 1.0);
Vc::double_v out2 = v_c + vFactor * (v_mz + v_pz +
v_my + v_py +
v_mx + v_px +
- 6.0 * v_c ) +
deltaT * u_c * v_c * v_c +
out1.store(&U_new.get<0>(Cp),Vc::Unaligned);
out2.store(&V_new.get<0>(Cp),Vc::Unaligned);
END_LOOP_M(Vc::double_v::Size)
- Another possibility is to use FORTRAN. Because FORTRAN has better support for multi dimensional array another possibility is to process each local grid using FORTRAN, this also give us the opportunity to show hybrid code. We can switch between one and the other method commenting and uncommeting the line #define FORTRAN_UPDATE in the code.
auto & ginfo = OldU.getLocalGridsInfo();
for (size_t i = 0 ; i < OldU.getN_loc_grid() ; i++)
{
auto & U_old = OldU.get_loc_grid(i);
auto & V_old = OldV.get_loc_grid(i);
auto & U_new = NewU.get_loc_grid(i);
auto & V_new = NewV.get_loc_grid(i);
int lo[3] = {(
int)ginfo.get(i).Dbox.getLow(0),(
int)ginfo.get(i).Dbox.getLow(1),(
int)ginfo.get(i).Dbox.getLow(2)};
int hi[3] = {(
int)ginfo.get(i).Dbox.getHigh(0),(
int)ginfo.get(i).Dbox.getHigh(1),(
int)ginfo.get(i).Dbox.getHigh(2)};
int ulo[3] = {0,0,0};
int uhi[3] = {(
int)ginfo.get(i).GDbox.getHigh(0),(
int)ginfo.get(i).GDbox.getHigh(1),(
int)ginfo.get(i).GDbox.getHigh(2)};
int nulo[3] = {0,0,0};
int nuhi[3] = {(
int)ginfo.get(i).GDbox.getHigh(0),(
int)ginfo.get(i).GDbox.getHigh(1),(
int)ginfo.get(i).GDbox.getHigh(2)};
int vlo[3] = {0,0,0};
int vhi[3] = {(
int)ginfo.get(i).GDbox.getHigh(0),(
int)ginfo.get(i).GDbox.getHigh(1),(
int)ginfo.get(i).GDbox.getHigh(2)};
int nvlo[3] = {0,0,0};
int nvhi[3] = {(
int)ginfo.get(i).GDbox.getHigh(0),(
int)ginfo.get(i).GDbox.getHigh(1),(
int)ginfo.get(i).GDbox.getHigh(2)};
update_new(lo,hi,
(double *)U_old.getPointer(),ulo,uhi,
(double *)V_old.getPointer(),vlo,vhi,
(double *)U_new.getPointer(),nulo,nuhi,
(double *)V_new.getPointer(),nulo,nvhi,
&deltaT, &uFactor_s, &vFactor_s,&
F,&K);
}
KeyT const ValueT ValueT OffsetIteratorT OffsetIteratorT int
[in] The number of segments that comprise the sorting data
subroutine update_new ( &
lo, hi, &
u, ulo, uhi, &
v, vlo, vhi, &
u_new, nulo, nuhi, &
v_new, nvlo, nvhi, &
dt, uFactor, vFactor,F,Kf) bind(C, name="update_new")
implicit none
integer, intent(in) :: lo(3), hi(3)
integer, intent(in) :: ulo(3), uhi(3)
integer, intent(in) :: vlo(3), vhi(3)
integer, intent(in) :: nulo(3), nuhi(3), nvlo(3), nvhi(3)
real*8, intent(in) :: u(ulo(1):uhi(1),ulo(2):uhi(2),ulo(3):uhi(3))
real*8, intent(in) :: v(vlo(1):vhi(1),vlo(2):vhi(2),vlo(3):vhi(3))
real*8, intent(inout) :: u_new( nulo(1): nuhi(1), nulo(2): nuhi(2), nulo(3): nuhi(3))
real*8, intent(inout) :: v_new( nvlo(1): nvhi(1), nvlo(2): nvhi(2), nvlo(3): nvhi(3))
real*8, intent(in) :: dt, f, kf, ufactor, vfactor
integer i,j,k
do k = lo(3), hi(3)
do j = lo(2), hi(2)
do i = lo(1), hi(1)
u_new(i,j,k) = u(i,j,k) + ufactor * ( u(i+1,j,k) + u(i-1,j,k) + &
u(i,j+1,k) + u(i,j-1,k) + &
u(i,j,k-1) + u(i,j,k+1) - &
6.0*u(i,j,k) ) - &
dt * u(i,j,k)*v(i,j,k)*v(i,j,k) - &
dt * f * (u(i,j,k) - 1.0)
v_new(i,j,k) = v(i,j,k) + vfactor * ( v(i+1,j,k) + v(i-1,j,k) + &
v(i,j+1,k) + v(i,j-1,k) + &
v(i,j,k-1) + v(i,j,k+1) - &
6.0*v(i,j,k) ) + &
dt * u(i,j,k)*v(i,j,k)*v(i,j,k) - &
dt * (f+kf) * v(i,j,k)
end do
end do
end do
end subroutine update_new
Instead of using the function write we use the function save to save on HDF5
Finalize
Deinitialize the library
Full code
#include "Grid/grid_dist_id.hpp"
#include "data_type/aggregate.hpp"
#include "timer.hpp"
#define FORTRAN_UPDATE
#ifndef FORTRAN_UPDATE
#include "Vc/Vc"
#endif
constexpr int x = 0;
constexpr int y = 1;
constexpr int z = 2;
extern "C" void update_new(const int* lo, const int* hi,
double* u, const int* ulo, const int* uhi,
double* v, const int* vlo, const int* vhi,
double* flu, const int* fulo, const int* fuhi,
double* flv, const int* fvlo, const int* fvhi,
const double * dt,
const double * uFactor,
const double * vFactor,
const double *
F,
const double * K);
{
auto it = OldU.getDomainIterator();
while (it.isNext())
{
auto key = it.get();
OldU.get<0>(key) = 1.0;
OldV.get<0>(key) = 0.0;
NewU.get<0>(key) = 0.0;
NewV.get<0>(key) = 0.0;
++it;
}
long int x_start = OldU.size(0)*1.55f/domain.getHigh(0);
long int y_start = OldU.size(1)*1.55f/domain.getHigh(1);
long int z_start = OldU.size(1)*1.55f/domain.getHigh(2);
long int x_stop = OldU.size(0)*1.85f/domain.getHigh(0);
long int y_stop = OldU.size(1)*1.85f/domain.getHigh(1);
long int z_stop = OldU.size(1)*1.85f/domain.getHigh(2);
auto it_init = OldU.getSubDomainIterator(start,stop);
while (it_init.isNext())
{
auto key = it_init.
get();
OldU.get<0>(key) = 0.5 + (((double)std::rand())/RAND_MAX -0.5)/10.0;
OldV.get<0>(key) = 0.25 + (((double)std::rand())/RAND_MAX -0.5)/20.0;
++it_init;
}
}
double uFactor_s,
double vFactor_s,
double deltaT,
double F,
double K)
{
#ifndef FORTRAN_UPDATE
Vc::double_v uFactor = uFactor_s;
Vc::double_v vFactor = vFactor_s;
WHILE_M(OldU,star_stencil_3D)
auto & U_old = GET_GRID_M(OldU);
auto & V_old = GET_GRID_M(OldV);
auto & U_new = GET_GRID_M(NewU);
auto & V_new = GET_GRID_M(NewV);
ITERATE_3D_M(Vc::double_v::Size)
auto Cp = it.getStencil<0>();
auto mx = it.getStencil<1>();
auto px = it.getStencil<2>();
auto my = it.getStencil<3>();
auto py = it.getStencil<4>();
auto mz = it.getStencil<5>();
auto pz = it.getStencil<6>();
Vc::double_v u_c(&U_old.get<0>(Cp),Vc::Unaligned);
Vc::double_v u_mz(&U_old.get<0>(mz),Vc::Unaligned);
Vc::double_v u_pz(&U_old.get<0>(pz),Vc::Unaligned);
Vc::double_v u_my(&U_old.get<0>(my),Vc::Unaligned);
Vc::double_v u_py(&U_old.get<0>(py),Vc::Unaligned);
Vc::double_v u_mx(&U_old.get<0>(mx),Vc::Unaligned);
Vc::double_v u_px(&U_old.get<0>(px),Vc::Unaligned);
Vc::double_v v_c(&V_old.get<0>(Cp),Vc::Unaligned);
Vc::double_v v_mz(&V_old.get<0>(mz),Vc::Unaligned);
Vc::double_v v_pz(&V_old.get<0>(pz),Vc::Unaligned);
Vc::double_v v_my(&V_old.get<0>(my),Vc::Unaligned);
Vc::double_v v_py(&V_old.get<0>(py),Vc::Unaligned);
Vc::double_v v_mx(&V_old.get<0>(mx),Vc::Unaligned);
Vc::double_v v_px(&V_old.get<0>(px),Vc::Unaligned);
Vc::double_v out1 = u_c + uFactor * (u_mz + u_pz +
u_my + u_py +
u_mx + u_px +
- 6.0 * u_c) +
- deltaT * u_c * v_c * v_c
- deltaT *
F * (u_c - 1.0);
Vc::double_v out2 = v_c + vFactor * (v_mz + v_pz +
v_my + v_py +
v_mx + v_px +
- 6.0 * v_c ) +
deltaT * u_c * v_c * v_c +
out1.store(&U_new.get<0>(Cp),Vc::Unaligned);
out2.store(&V_new.get<0>(Cp),Vc::Unaligned);
END_LOOP_M(Vc::double_v::Size)
#else
auto & ginfo = OldU.getLocalGridsInfo();
for (size_t i = 0 ; i < OldU.getN_loc_grid() ; i++)
{
auto & U_old = OldU.get_loc_grid(i);
auto & V_old = OldV.get_loc_grid(i);
auto & U_new = NewU.get_loc_grid(i);
auto & V_new = NewV.get_loc_grid(i);
int lo[3] = {(
int)ginfo.get(i).Dbox.getLow(0),(
int)ginfo.get(i).Dbox.getLow(1),(
int)ginfo.get(i).Dbox.getLow(2)};
int hi[3] = {(
int)ginfo.get(i).Dbox.getHigh(0),(
int)ginfo.get(i).Dbox.getHigh(1),(
int)ginfo.get(i).Dbox.getHigh(2)};
int ulo[3] = {0,0,0};
int uhi[3] = {(
int)ginfo.get(i).GDbox.getHigh(0),(
int)ginfo.get(i).GDbox.getHigh(1),(
int)ginfo.get(i).GDbox.getHigh(2)};
int nulo[3] = {0,0,0};
int nuhi[3] = {(
int)ginfo.get(i).GDbox.getHigh(0),(
int)ginfo.get(i).GDbox.getHigh(1),(
int)ginfo.get(i).GDbox.getHigh(2)};
int vlo[3] = {0,0,0};
int vhi[3] = {(
int)ginfo.get(i).GDbox.getHigh(0),(
int)ginfo.get(i).GDbox.getHigh(1),(
int)ginfo.get(i).GDbox.getHigh(2)};
int nvlo[3] = {0,0,0};
int nvhi[3] = {(
int)ginfo.get(i).GDbox.getHigh(0),(
int)ginfo.get(i).GDbox.getHigh(1),(
int)ginfo.get(i).GDbox.getHigh(2)};
update_new(lo,hi,
(double *)U_old.getPointer(),ulo,uhi,
(double *)V_old.getPointer(),vlo,vhi,
(double *)U_new.getPointer(),nulo,nuhi,
(double *)V_new.getPointer(),nulo,nvhi,
&deltaT, &uFactor_s, &vFactor_s,&
F,&K);
}
#endif
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
openfpm_init(&argc,&argv);
size_t sz[3] = {128,128,128};
double deltaT = 1.0;
double du = 2*1e-5;
double dv = 1*1e-5;
size_t timeSteps = 5000;
double K = 0.053;
double spacing[3] = {OldU.spacing(0),OldU.spacing(1),OldU.spacing(2)};
init(OldU,OldV,NewU,NewV,domain);
size_t count = 0;
OldU.template ghost_get<0>();
OldV.template ghost_get<0>();
double uFactor = deltaT * du/(spacing[x]*spacing[x]);
double vFactor = deltaT * dv/(spacing[x]*spacing[x]);
auto & v_cl = create_vcluster();
{0,0,-1},
{0,0,1},
{0,-1,0},
{0,1,0},
{-1,0,0},
{1,0,0}};
for (size_t i = 0; i < timeSteps; ++i)
{
if (i % 100 == 0 && v_cl.rank() == 0)
{
std::cout << "STEP: " << i << std::endl;
}
if (i % 2 == 0)
{
step(OldU,OldV,NewU,NewV,star_stencil_3D,uFactor,vFactor,deltaT,
F,K);
NewU.ghost_get<0>();
NewV.ghost_get<0>();
}
else
{
step(NewU,NewV,OldU,OldV,star_stencil_3D,uFactor,vFactor,deltaT,
F,K);
OldU.ghost_get<0>();
OldV.ghost_get<0>();
}
}
if (create_vcluster().rank() == 0)
{std::cout <<
"Total simulation: " << tot_sim.
getwct() << std::endl;}
OldV.write("final");
openfpm_finalize();
}
This class represent an N-dimensional box.
grid_key_dx is the key to access any element in the grid
__device__ __host__ index_type get(index_type i) const
Get the i index.
Class for cpu time benchmarking.
void stop()
Stop the timer.
void start()
Start the timer.
double getwct()
Return the elapsed real time.
aggregate of properties, from a list of object if create a struct that follow the OPENFPM native stru...
