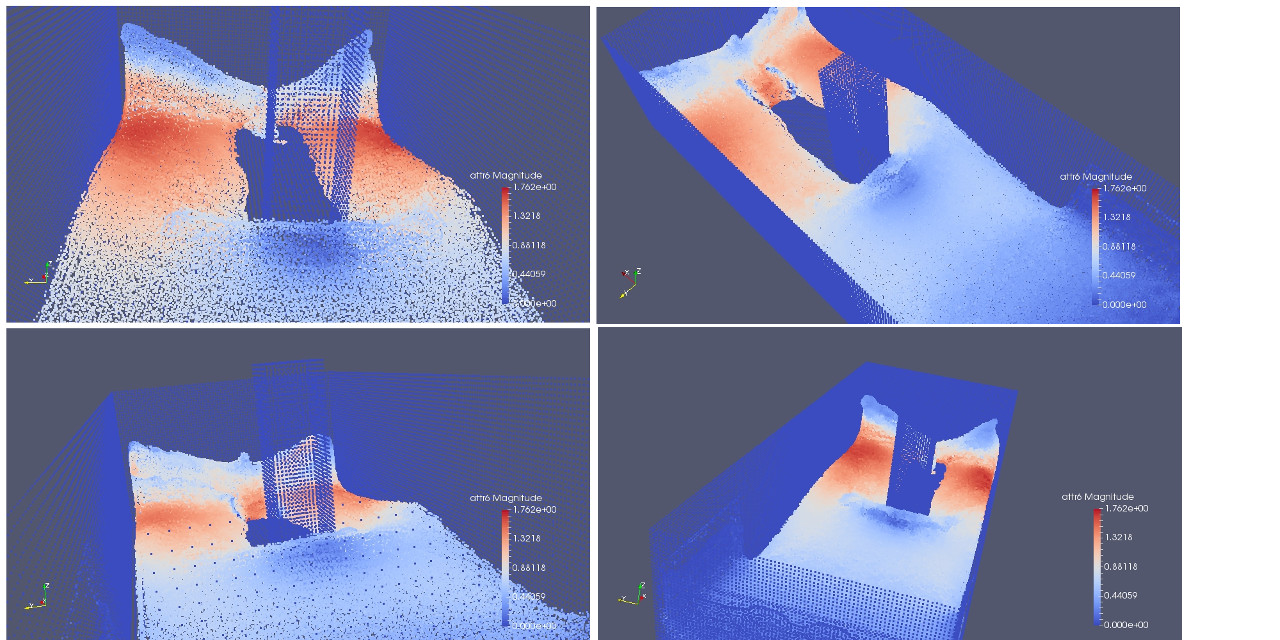
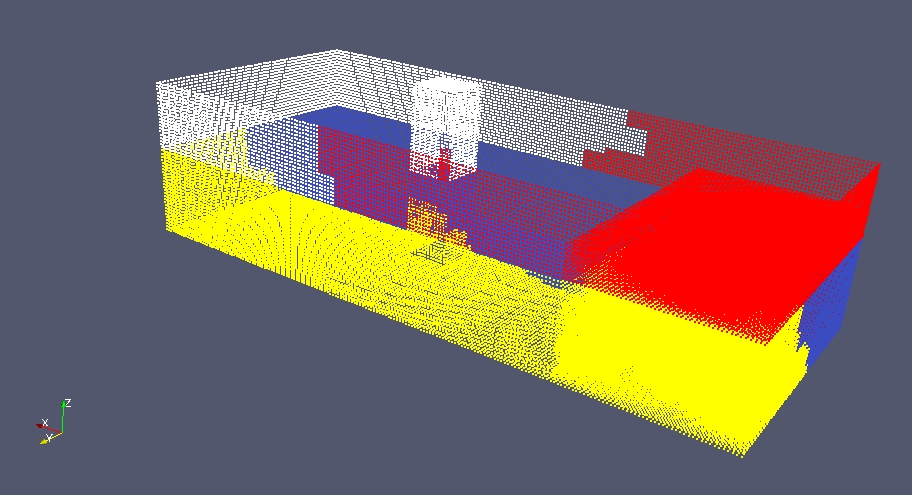
This example show the classical SPH Dam break simulation with Load Balancing and Dynamic load balancing. With Load balancing and Dynamic load balancing we indicate the possibility of the system to re-adapt the domain decomposition to keep all the processor load and reduce idle time.
Simulation video 1
Simulation video 2
Simulation dynamic load balancing video 1
Simulation dynamic load balancing video 2
Simulation countour prospective 1
Simulation countour prospective 2
Simulation countour prospective 3
In order to use distributed vectors in our code we have to include the file Vector/vector_dist.hpp we also include DrawParticles that has nice utilities to draw particles in parallel accordingly to simple shapes
#include "Vector/vector_dist.hpp"
#include <math.h>
#include "Draw/DrawParticles.hpp"
The SPH formulation used in this example code follow these equations
\(\frac{dv_a}{dt} = - \sum_{b = NN(a) } m_b \left(\frac{P_a + P_b}{\rho_a \rho_b} + \Pi_{ab} \right) \nabla_{a} W_{ab} + g \tag{1} \)
\(\frac{d\rho_a}{dt} = \sum_{b = NN(a) } m_b v_{ab} \cdot \nabla_{a} W_{ab} \tag{2} \)
\( P_a = b \left[ \left( \frac{\rho_a}{\rho_{0}} \right)^{\gamma} - 1 \right] \tag{3} \)
with
\( \Pi_{ab} = \begin{cases} - \frac {\alpha \bar{c_{ab}} \mu_{ab} }{\bar{\rho_{ab}} } & v_{ab} \cdot r_{ab} > 0 \\ 0 & v_{ab} \cdot r_{ab} < 0 \end{cases} \tag{4}\)
and the constants defined as
\( b = \frac{c_{s}^{2} \rho_0}{\gamma} \tag{5} \)
\( c_s = \sqrt{g \cdot h_{swl}} \tag{6} \)
While the particle kernel support is given by
\( H = \sqrt{3 \cdot dp} \tag{7} \)
Explain the equations is out of the context of this tutorial. An introduction can be found regarding SPH in general in the original Monghagan SPH paper. In this example we use the sligtly modified version used by Dual-SPH (http://www.dual.sphysics.org/ ). A summary of the equation and constants can be founded in their User Manual and the XML user Manual.
Based on the equation reported before several constants must be defined.
#define BOUNDARY 0
#define FLUID 1
const double dp = 0.0085;
double h_swl = 0.0;
const double coeff_sound = 20.0;
const double gamma_ = 7.0;
const double H = 0.0147224318643;
const double Eta2 = 0.01 * H*H;
const double visco = 0.1;
double cbar = 0.0;
const double MassFluid = 0.000614125;
const double MassBound = 0.000614125;
#ifdef TEST_RUN
const double t_end = 0.001;
#else
const double t_end = 1.5;
#endif
const double gravity = 9.81;
const double rho_zero = 1000.0;
double B = 0.0;
const double CFLnumber = 0.2;
const double DtMin = 0.00001;
const double RhoMin = 700.0;
const double RhoMax = 1300.0;
double max_fluid_height = 0.0;
const size_t type = 0;
const int rho = 1;
const int rho_prev = 2;
const int Pressure = 3;
const int drho = 4;
const int force = 5;
const int velocity = 6;
const int velocity_prev = 7;
This function implement the formula 3 in the set of equations. It calculate the pressure of each particle based on the local density of each particle.
{
while (it.isNext())
{
auto a = it.get();
double rho_a = vd.template getProp<rho>(a);
double rho_frac = rho_a / rho_zero;
vd.template getProp<Pressure>(a) = B*( rho_frac*rho_frac*rho_frac*rho_frac*rho_frac*rho_frac*rho_frac - 1.0);
++it;
}
}
vector_dist_iterator getDomainIterator() const
Get an iterator that traverse the particles in the domain.
This function define the Cubic kernel or \( W_{ab} \). The cubic kernel is defined as
\( \begin{cases} 1.0 - \frac{3}{2} q^2 + \frac{3}{4} q^3 & 0 < q < 1 \\ (2 - q)^3 & 1 < q < 2 \\ 0 & q > 2 \end{cases} \)
const double a2 = 1.0/M_PI/H/H/H;
inline double Wab(double r)
{
r /= H;
if (r < 1.0)
return (1.0 - 3.0/2.0*r*r + 3.0/4.0*r*r*r)*a2;
else if (r < 2.0)
return (1.0/4.0*(2.0 - r)*(2.0 - r)*(2.0 - r))*a2;
else
return 0.0;
}
This function define the gradient of the Cubic kernel function \( W_{ab} \).
\( \nabla W_{ab} = \beta (x,y,z) \)
\( \beta = \begin{cases} (c_1 q + d_1 q^2) & 0 < q < 1 \\ c_2 (2 - q)^2 & 1 < q < 2 \end{cases} \)
const double c1 = -3.0/M_PI/H/H/H/H;
const double d1 = 9.0/4.0/M_PI/H/H/H/H;
const double c2 = -3.0/4.0/M_PI/H/H/H/H;
const double a2_4 = 0.25*a2;
double W_dap = 0.0;
{
const double qq=r/H;
double qq2 = qq * qq;
double fac1 = (c1*qq + d1*qq2)/r;
double b1 = (qq < 1.0)?1.0f:0.0f;
double wqq = (2.0 - qq);
double fac2 = c2 * wqq * wqq / r;
double b2 = (qq >= 1.0 && qq < 2.0)?1.0f:0.0f;
double factor = (b1*fac1 + b2*fac2);
DW.
get (0) = factor * dx.
get (0);
DW.
get (1) = factor * dx.
get (1);
DW.
get (2) = factor * dx.
get (2);
}
This class implement the point shape in an N-dimensional space.
__device__ __host__ const T & get(unsigned int i) const
Get coordinate.
This function define the Tensile term. An explanation of the Tensile term is out of the context of this tutorial, but in brief is an additional repulsive term that avoid the particles to get too near. Can be considered at small scale like a repulsive force that avoid particles to get too close like the Lennard-Jhonned potential at atomistic level. A good reference is the Monaghan paper "SPH without a Tensile Instability"
inline double Tensile(double r, double rhoa, double rhob, double prs1, double prs2)
{
const double qq=r/H;
double wab;
if (r>H)
{
double wqq1=2.0f-qq;
double wqq2=wqq1*wqq1;
wab=a2_4*(wqq2*wqq1);
}
else
{
double wqq2=qq*qq;
double wqq3=wqq2*qq;
wab=a2*(1.0f-1.5f*wqq2+0.75f*wqq3);
}
double fab=wab*W_dap;
fab*=fab; fab*=fab;
const double tensilp1=(prs1/(rhoa*rhoa))*(prs1>0? 0.01: -0.2);
const double tensilp2=(prs2/(rhob*rhob))*(prs2>0? 0.01: -0.2);
return (fab*(tensilp1+tensilp2));
}
This function implement the viscous term \( \Pi_{ab} \)
{
const double dot_rr2 = dot/(rr2+Eta2);
visc=std::max(dot_rr2,visc);
if (dot < 0)
{
const float amubar=H*dot_rr2;
const float robar=(rhoa+rhob)*0.5f;
const float pi_visc=(-visco*cbar*amubar/robar);
return pi_visc;
}
else
return 0.0;
}
Calculate forces. It calculate equation 1 and 2 in the set of formulas
template <
typename CellList>
inline void calc_forces(
particles & vd,
CellList & NN,
double & max_visc)
{
while (part.isNext())
{
auto a = part.get();
double massa = (vd.
getProp <type>(a) == FLUID)?MassFluid:MassBound;
double Pa = vd.
getProp <Pressure>(a);
vd.template getProp<force>(a)[0] = 0.0;
vd.template getProp<force>(a)[1] = 0.0;
vd.template getProp<force>(a)[2] = -gravity;
vd.template getProp<drho>(a) = 0.0;
{
auto Np = NN.getNNIteratorBox(NN.getCell(vd.
getPos (a)));
while (Np.isNext() == true )
{
auto b = Np.get();
if (a.getKey() == b) {++Np; continue ;};
double massb = (vd.
getProp <type>(b) == FLUID)?MassFluid:MassBound;
double Pb = vd.
getProp <Pressure>(b);
double r2 = norm2(dr);
if (r2 < 4.0*H*H)
{
double r = sqrt(r2);
DWab(dr,DW,r,false );
const double dot = dr.get(0)*dv.
get (0) + dr.get(1)*dv.
get (1) + dr.get(2)*dv.
get (2);
const double dot_rr2 = dot/(r2+Eta2);
max_visc=std::max(dot_rr2,max_visc);
}
++Np;
}
}
else
{
auto Np = NN.getNNIteratorBox(NN.getCell(vd.
getPos (a)));
while (Np.isNext() == true )
{
auto b = Np.get();
if (a.getKey() == b) {++Np; continue ;};
double massb = (vd.
getProp <type>(b) == FLUID)?MassFluid:MassBound;
double Pb = vd.
getProp <Pressure>(b);
double r2 = norm2(dr);
if (r2 < 4.0*H*H)
{
double r = sqrt(r2);
DWab(dr,DW,r,false );
double factor = - massb*((vd.
getProp <Pressure>(a) + vd.
getProp <Pressure>(b)) / (rhoa * rhob) + Tensile(r,rhoa,rhob,Pa,Pb) + Pi(dr,r2,v_rel,rhoa,rhob,massb,max_visc));
}
++Np;
}
}
++part;
}
}
Class for FAST cell list implementation.
auto getProp(vect_dist_key_dx vec_key) -> decltype(vPrp.template get< id >(vec_key.getKey()))
Get the property of an element.
void updateCellList(CellL &cellList, bool no_se3=false)
Update a cell list using the stored particles.
auto getPos(vect_dist_key_dx vec_key) -> decltype(vPos.template get< 0 >(vec_key.getKey()))
Get the position of an element.
This function calculate the Maximum acceleration and velocity across the particles. It is used to calculate a dynamic time-stepping.
void max_acceleration_and_velocity(
particles & vd,
double & max_acc,
double & max_vel)
{
while (part.isNext())
{
auto a = part.get();
double acc2 = norm2(acc);
double vel2 = norm2(vel);
if (vel2 >= max_vel)
max_vel = vel2;
if (acc2 >= max_acc)
max_acc = acc2;
++part;
}
max_acc = sqrt(max_acc);
max_vel = sqrt(max_vel);
}
void execute()
Execute all the requests.
void max(T &num)
Get the maximum number across all processors (or reduction with infinity norm)
Implementation of VCluster class.
In this example we are using Dynamic time-stepping. The Dynamic time stepping is calculated with the Courant-Friedrich-Lewy condition. See Monaghan 1992 "Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamic"
\( \delta t = CFL \cdot min(t_f,t_{cv}) \)
where
\( \delta t_f = min \sqrt{h/f_a}\)
\( \delta t_{cv} = min \frac{h}{c_s + max \left| \frac{hv_{ab} \cdot r_{ab}}{r_{ab}^2} \right|} \)
double calc_deltaT(
particles & vd,
double ViscDtMax)
{
double Maxacc = 0.0;
double Maxvel = 0.0;
max_acceleration_and_velocity(vd,Maxacc,Maxvel);
const double dt_f = (Maxacc)?sqrt(H/Maxacc):std::numeric_limits<int>::max();
const double dt_cv = H/(std::max(cbar,Maxvel*10.) + H*ViscDtMax);
double dt=double(CFLnumber)*std::min(dt_f,dt_cv);
if (dt<double (DtMin))
dt=double(DtMin);
return dt;
}
This function perform verlet integration accordingly to the Verlet time stepping scheme
\( v_a^{n+1} = v_a^{n-1} + 2 \delta t F_a^{n} \)
\( r_a^{n+1} = \delta t V_a^n + 0.5 \delta t^2 F_a^n \)
\( \rho_a^{n+1} = \rho_a^{n-1} + 2 \delta t D_a^n \)
Every N Verlet steps the euler stepping scheme is choosen to avoid instabilities
\( v_a^{n+1} = v_a^{n} + \delta t F_a^n \)
\( r_a^{n+1} = r_a^{n} + \delta t V_a^n + \frac{1}{2} \delta t^2 F_a^n \)
\( \rho_a^{n+1} = \rho_a^n + \delta t D_a^n \)
This function also check that no particles go outside the simulation domain or their density go dangerously out of range. If a particle go out of range is removed from the simulation
size_t cnt = 0;
{
to_remove.clear();
double dt205 = dt*dt*0.5;
double dt2 = dt*2.0;
while (part.isNext())
{
auto a = part.get();
if (vd.template getProp<type>(a) == BOUNDARY)
{
double rhop = vd.template getProp<rho>(a);
vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[0] = 0.0;
vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[1] = 0.0;
vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[2] = 0.0;
double rhonew = vd.template getProp<rho_prev>(a) + dt2*vd.template getProp<drho>(a);
vd.template getProp<rho>(a) = (rhonew < rho_zero)?rho_zero:rhonew;
vd.template getProp<rho_prev>(a) = rhop;
++part;
continue ;
}
double dx = vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[0]*dt + vd.template getProp<force>(a)[0]*dt205;
double dy = vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[1]*dt + vd.template getProp<force>(a)[1]*dt205;
double dz = vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[2]*dt + vd.template getProp<force>(a)[2]*dt205;
double velX = vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[0];
double velY = vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[1];
double velZ = vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[2];
double rhop = vd.template getProp<rho>(a);
vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[0] = vd.template getProp<velocity_prev>(a)[0] + vd.template getProp<force>(a)[0]*dt2;
vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[1] = vd.template getProp<velocity_prev>(a)[1] + vd.template getProp<force>(a)[1]*dt2;
vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[2] = vd.template getProp<velocity_prev>(a)[2] + vd.template getProp<force>(a)[2]*dt2;
vd.template getProp<rho>(a) = vd.template getProp<rho_prev>(a) + dt2*vd.template getProp<drho>(a);
if (vd.
getPos (a)[0] < 0.000263878 || vd.
getPos (a)[1] < 0.000263878 || vd.
getPos (a)[2] < 0.000263878 ||
vd.
getPos (a)[0] > 0.000263878+1.59947 || vd.
getPos (a)[1] > 0.000263878+0.672972 || vd.
getPos (a)[2] > 0.000263878+0.903944 ||
vd.template getProp<rho>(a) < RhoMin || vd.template getProp<rho>(a) > RhoMax)
{
to_remove.add(a.getKey());
}
vd.template getProp<velocity_prev>(a)[0] = velX;
vd.template getProp<velocity_prev>(a)[1] = velY;
vd.template getProp<velocity_prev>(a)[2] = velZ;
vd.template getProp<rho_prev>(a) = rhop;
++part;
}
cnt++;
}
{
to_remove.clear();
double dt205 = dt*dt*0.5;
double dt2 = dt*2.0;
while (part.isNext())
{
auto a = part.get();
if (vd.template getProp<type>(a) == BOUNDARY)
{
double rhop = vd.template getProp<rho>(a);
vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[0] = 0.0;
vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[1] = 0.0;
vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[2] = 0.0;
double rhonew = vd.template getProp<rho>(a) + dt*vd.template getProp<drho>(a);
vd.template getProp<rho>(a) = (rhonew < rho_zero)?rho_zero:rhonew;
vd.template getProp<rho_prev>(a) = rhop;
++part;
continue ;
}
double dx = vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[0]*dt + vd.template getProp<force>(a)[0]*dt205;
double dy = vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[1]*dt + vd.template getProp<force>(a)[1]*dt205;
double dz = vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[2]*dt + vd.template getProp<force>(a)[2]*dt205;
double velX = vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[0];
double velY = vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[1];
double velZ = vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[2];
double rhop = vd.template getProp<rho>(a);
vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[0] = vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[0] + vd.template getProp<force>(a)[0]*dt;
vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[1] = vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[1] + vd.template getProp<force>(a)[1]*dt;
vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[2] = vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[2] + vd.template getProp<force>(a)[2]*dt;
vd.template getProp<rho>(a) = vd.template getProp<rho>(a) + dt*vd.template getProp<drho>(a);
if (vd.
getPos (a)[0] < 0.000263878 || vd.
getPos (a)[1] < 0.000263878 || vd.
getPos (a)[2] < 0.000263878 ||
vd.
getPos (a)[0] > 0.000263878+1.59947 || vd.
getPos (a)[1] > 0.000263878+0.672972 || vd.
getPos (a)[2] > 0.000263878+0.903944 ||
vd.template getProp<rho>(a) < RhoMin || vd.template getProp<rho>(a) > RhoMax)
{
to_remove.add(a.getKey());
}
vd.template getProp<velocity_prev>(a)[0] = velX;
vd.template getProp<velocity_prev>(a)[1] = velY;
vd.template getProp<velocity_prev>(a)[2] = velZ;
vd.template getProp<rho_prev>(a) = rhop;
++part;
}
cnt++;
}
void remove(std::set< size_t > &keys)
Remove a set of elements from the distributed vector.
This function show how to create a pressure sensor/probe on a set of specified points. To do this from the cell-list we just get an iterator across the neighborhood points of the sensors and we calculate the pressure profile. On the other hand because the sensor is in the processor domain of only one processor, only one processor must do this calculation. We will use the function isLocal to determine which processor contain the probe and only such processor will do the calculation.
Warning This type of calculation is suitable if the number of probes is small (like 10) and pressure is not calculated every time step. In case the number of probes is comparable to the number of particles or the pressure is calculated every time-step than we suggest to create a set of "probe" particles
template <typename Vector, typename CellList>
inline void sensor_pressure(
Vector & vd,
{
press_t.add();
for (size_t i = 0 ; i < probes.size() ; i++)
{
float press_tmp = 0.0f;
float tot_ker = 0.0;
if (vd.getDecomposition().isLocal(probes.get(i)) == true )
{
auto itg = NN.getNNIteratorBox(NN.getCell(probes.get(i)));
while (itg.isNext())
{
auto q = itg.get();
if (vd.template getProp<type>(q) != FLUID)
{
++itg;
continue ;
}
double r = sqrt(norm2(xp - xq));
double ker = Wab(r) * (MassFluid / rho_zero);
tot_ker += ker;
press_tmp += vd.template getProp<Pressure>(q) * ker;
++itg;
}
if (tot_ker == 0.0)
press_tmp = 0.0;
else
press_tmp = 1.0 / tot_ker * press_tmp;
}
press_t.last().add(press_tmp);
}
}
void sum(T &num)
Sum the numbers across all processors and get the result.
Sparse Matrix implementation stub object when OpenFPM is compiled with no linear algebra support.
Here we Initialize the library, we create a Box that define our domain, boundary conditions and ghost. We also create a vector that contain two probes to measure pressure
See also Initialization
openfpm_init(&argc,&argv);
probes.add({0.8779,0.3,0.02});
probes.add({0.754,0.31,0.02});
Box<3,double> domain({-0.05,-0.05,-0.05},{1.7010,0.7065,0.5025});
size_t sz[3] = {207,90,66};
W_dap = 1.0/Wab(H/1.5);
size_t bc[3]={NON_PERIODIC,NON_PERIODIC,NON_PERIODIC};
This class represent an N-dimensional box.
Here we define a distributed vector in 3D , we use the particles type that we defined previously. Each particle contain the following properties
type Type of the particlerho Density of the particlerho_prev Density at previous timestepPressure Pressure of the particledrho Derivative of the density over timeforce acceleration of the particlesvelocity velocity of the particlesvelocity_prev velocity of the particles at previous time-step
In this case the vector contain 0 particles initially
See also Vector instantiation The option DEC_GRAN(512) is related to the Load-Balancing decomposition granularity. It indicate that the space must be decomposed by at least
\( N_{subsub} = 512 \cdot N_p \)
Where \( N_{subsub} \) is the number of sub-sub-domain in which the space must be decomposed and \( N_p \) is the number of processors. (The concept of sub-sub-domain will be explained leter)
In this part we initialize the problem creating particles. In order to do it we use the class DrawParticles . Because some of the simulation constants require the maximum height \( h_{swl} \) of the fluid to be calculated and the maximum fluid height is determined at runtime, some of the constants just after we create the fluid particles
The Function DrawParticles::DrawBox return an iterator that can be used to create particle in a predefined box (smaller than the simulation domain) with a predefined spacing. We start drawing the fluid particles, the initial pressure is initialized accordingly to the Hydrostatic pressure given by:
\( P = \rho_{0} g (h_{max} - z) \)
Where \( h_{max} \) is the maximum height of the fluid. The density instead is given by the equation (3). Assuming \( \rho \) constant to \( \rho_{0} \) in the Hydrostatic equation is a good approximation. Velocity is initialized to zero.
See also Vector instantiation
Box<3,double> fluid_box({dp/2.0,dp/2.0,dp/2.0},{0.4+dp/2.0,0.67-dp/2.0,0.3+dp/2.0});
max_fluid_height = fluid_it.getBoxMargins().
getHigh (2);
h_swl = fluid_it.getBoxMargins().
getHigh (2) - fluid_it.getBoxMargins().
getLow (2);
B = (coeff_sound)*(coeff_sound)*gravity*h_swl*rho_zero / gamma_;
cbar = coeff_sound * sqrt(gravity * h_swl);
while (fluid_it.isNext())
{
vd.add();
vd.getLastPos()[0] = fluid_it.get().get(0);
vd.getLastPos()[1] = fluid_it.get().get(1);
vd.getLastPos()[2] = fluid_it.get().get(2);
vd.template getLastProp<type>() = FLUID;
vd.template getLastProp<Pressure>() = rho_zero * gravity * (max_fluid_height - fluid_it.get().get(2));
vd.template getLastProp<rho>() = pow(vd.template getLastProp<Pressure>() / B + 1, 1.0/gamma_) * rho_zero;
vd.template getLastProp<rho_prev>() = vd.template getLastProp<rho>();
vd.template getLastProp<velocity>()[0] = 0.0;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity>()[1] = 0.0;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity>()[2] = 0.0;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity_prev>()[0] = 0.0;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity_prev>()[1] = 0.0;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity_prev>()[2] = 0.0;
++fluid_it;
}
__device__ __host__ T getLow(int i) const
get the i-coordinate of the low bound interval of the box
__device__ __host__ T getHigh(int i) const
get the high interval of the box
static PointIterator< dim, T, typename vd_type::Decomposition_type > DrawBox(vd_type &vd, size_t(&sz)[dim], Box< dim, T > &domain, Box< dim, T > &sub)
Draw particles in a box.
Here we draw the recipient using the function DrawParticles::DrawSkin . This function can draw a set of particles inside a box A removed of a second box or an array of boxes. So all the particles in the area included in the area A - B - C. There is no restriction that B or C must be included into A.
In this case A is the box defining the recipient, B is the box cutting out the internal part of the recipient, C is the hole where we will place the obstacle. Because we use Dynamic boundary condition (DBC) we initialize the density to \( \rho_{0} \). It will be update over time according to equation (3) to keep the particles confined.
Box<3,double> recipient1({0.0,0.0,0.0},{1.6+dp/2.0,0.67+dp/2.0,0.4+dp/2.0});
Box<3,double> recipient2({dp,dp,dp},{1.6-dp/2.0,0.67-dp/2.0,0.4+dp/2.0});
Box<3,double> obstacle1({0.9,0.24-dp/2.0,0.0},{1.02+dp/2.0,0.36,0.45+dp/2.0});
Box<3,double> obstacle2({0.9+dp,0.24+dp/2.0,0.0},{1.02-dp/2.0,0.36-dp,0.45-dp/2.0});
holes.add(recipient2);
holes.add(obstacle1);
while (bound_box.isNext())
{
vd.add();
vd.getLastPos()[0] = bound_box.get().get(0);
vd.getLastPos()[1] = bound_box.get().get(1);
vd.getLastPos()[2] = bound_box.get().get(2);
vd.template getLastProp<type>() = BOUNDARY;
vd.template getLastProp<rho>() = rho_zero;
vd.template getLastProp<rho_prev>() = rho_zero;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity>()[0] = 0.0;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity>()[1] = 0.0;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity>()[2] = 0.0;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity_prev>()[0] = 0.0;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity_prev>()[1] = 0.0;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity_prev>()[2] = 0.0;
++bound_box;
}
static PointIteratorSkin< dim, T, typename vd_type::Decomposition_type > DrawSkin(vd_type &vd, size_t(&sz)[dim], Box< dim, T > &domain, Box< dim, T > &sub_A, Box< dim, T > &sub_B)
Draw particles in a box B excluding the area of a second box A (B - A)
Here we draw the obstacle in the same way we draw the recipient. also for the obstacle is valid the same concept of using Dynamic boundary condition (DBC)
while (obstacle_box.isNext())
{
vd.add();
vd.getLastPos()[0] = obstacle_box.get().get(0);
vd.getLastPos()[1] = obstacle_box.get().get(1);
vd.getLastPos()[2] = obstacle_box.get().get(2);
vd.template getLastProp<type>() = BOUNDARY;
vd.template getLastProp<rho>() = rho_zero;
vd.template getLastProp<rho_prev>() = rho_zero;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity>()[0] = 0.0;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity>()[1] = 0.0;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity>()[2] = 0.0;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity_prev>()[0] = 0.0;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity_prev>()[1] = 0.0;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity_prev>()[2] = 0.0;
++obstacle_box;
}
vd.map();
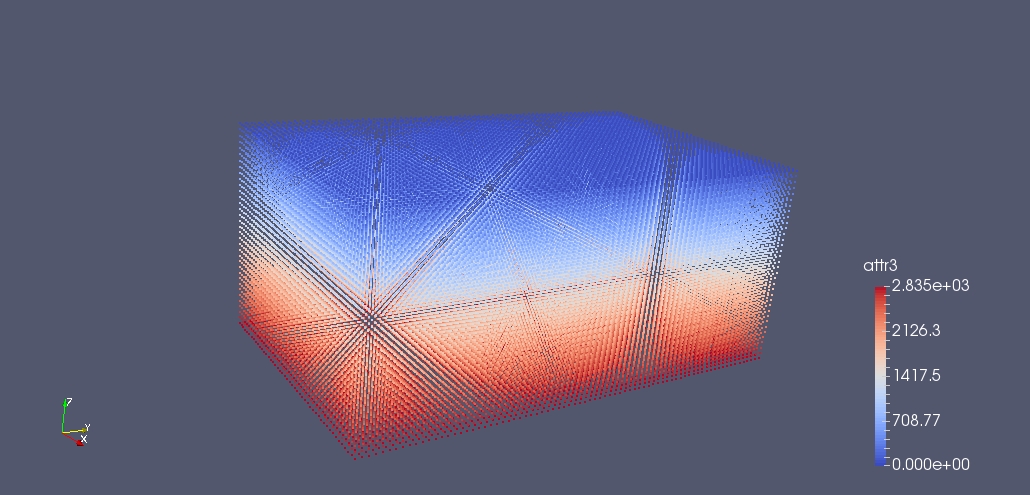
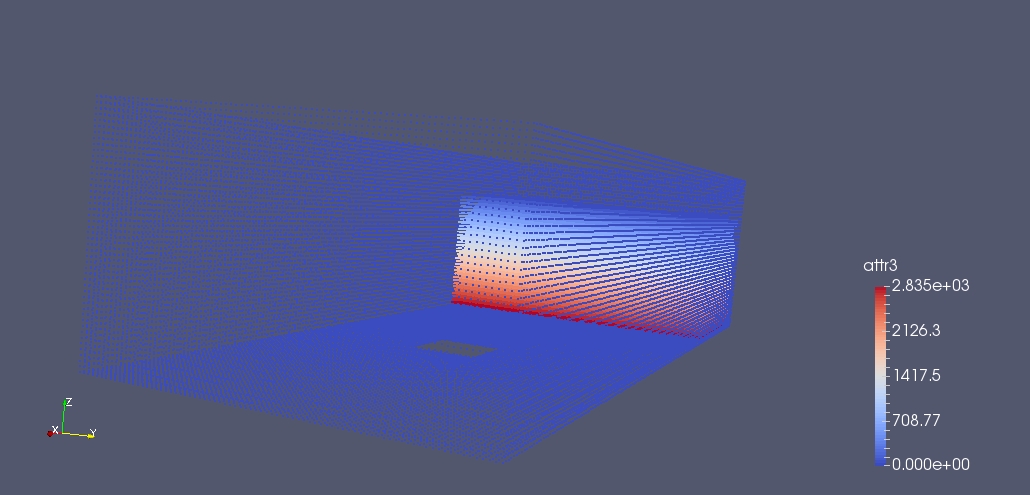
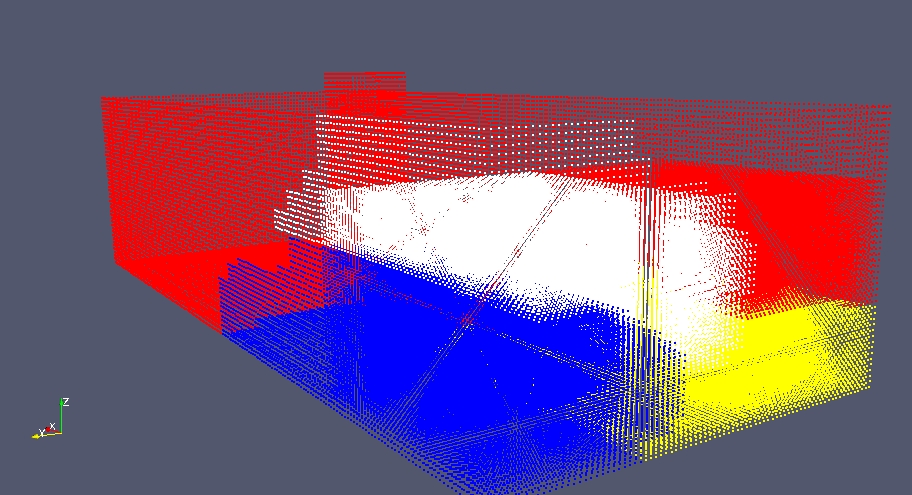
If at this point we output the particles and we visualize where they are accordingly to their processor id we can easily see that particles are distributed unevenly. The processor that has particles in white has few particles and all of them are non fluid. This mean that it will be almost in idle. This situation is not ideal
In order to reach an optimal situation we have to distribute the particles to reach a balanced situation. To do this we have to set the computation of each sub-sub-domain, redecompose the space and distribute the particles accordingly to this new configuration. To do this we need a model. A model specify how to set the computational cost for each sub-sub-domains (for example it specify if the computational cost to process a sub-sub-domain is quadratic or linear with the number of particles ...). A model look like this.
{
template <
typename Decomposition,
typename vector>
inline void addComputation(
Decomposition & dec,
vector & vd,
size_t v,
size_t p)
{
if (vd.template getProp<type>(p) == FLUID)
dec.addComputationCost(v,4);
else
dec.addComputationCost(v,3);
}
template <
typename Decomposition>
inline void applyModel(
Decomposition & dec,
size_t v)
{
dec.setSubSubDomainComputationCost(v, dec.getSubSubDomainComputationCost(v) * dec.getSubSubDomainComputationCost(v));
}
double distributionTol()
{
return 1.01;
}
};
This class define the domain decomposition interface.
Model for Dynamic load balancing.
Setting the the computational cost on sub-sub-domains is performed running across the particles. For each one of them, it is calculated on which sub-sub-domain it belong. Than the function addComputation is called. Inside this call we can set the weight in the way we prefer. In this case we set the weight as:
\( w_v = 4 N_{fluid} + 3 N_{boundary} \)
Where \( N_{fluid} \) Is the number of fluid particles in the sub-sub-domains and \( N_{boundary} \) are the number of boundary particles. For example in our ModelCustom we square this number, because the computation is proportional to the square of the number of particles in each sub-sub-domain. A second cycle is performed in order to calculate a complex function of this number (for example squaring).
Implicitly the communication cost is given by \( \frac{V_{ghost}}{V_{sub-sub}} t_s \), while the migration cost is given by \( v_{sub-sub} \). In general \( t_s \) is the number of ghost get between two rebalance. In this special case where we have two type of particles, we have two different computation for each of them, this mean that fluid particles and boundary particles has different computation cost.
After filling the computational cost based on our model we can decompose the problem in computationally equal chunk for each processor. We use the function decomposed to redecompose the space and subsequently we use the function map to redistribute the particles.
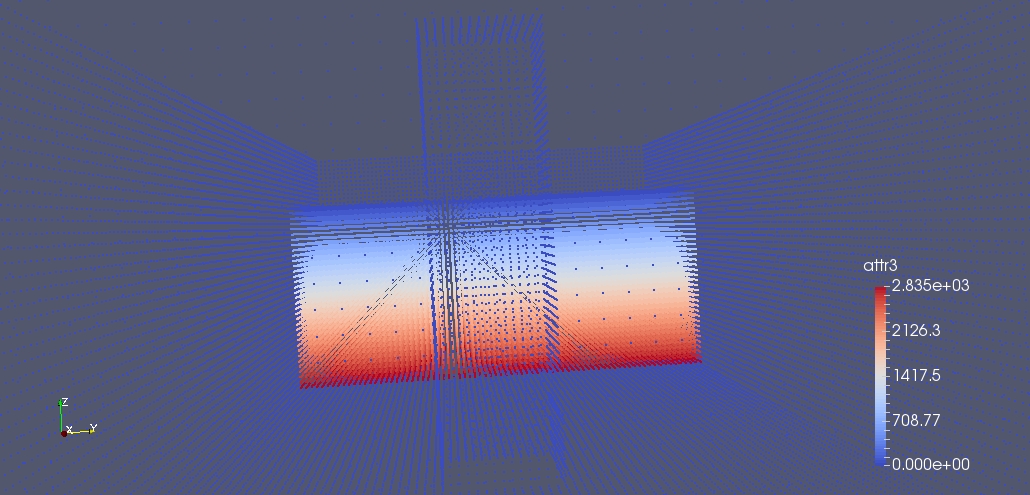
Note All processors now has part of the fluid. It is good to note that the computationaly balanced configuration does not correspond to the evenly distributed particles to know more about that please follow the video tutorials
Dynamic load balancing the theory part1
Dynamic load balancing the theory part2
Dynamic load balancing practice part1
Dynamic load balancing practice part2
vd.addComputationCosts(md);
vd.getDecomposition().decompose();
vd.map();
The main loop do time integration. It calculate the pressure based on the density, than calculate the forces, than we calculate delta time, and finally update position and velocity. After 200 time-step we do a re-balancing. We save the configuration and we calculate the pressure on the probe position every 0.01 seconds
size_t write = 0;
size_t it = 0;
size_t it_reb = 0;
double t = 0.0;
while (t <= t_end)
{
it_reb++;
if (it_reb == 200)
{
vd.map();
it_reb = 0;
vd.addComputationCosts(md);
vd.getDecomposition().decompose();
std::cout << "REBALANCED " << std::endl;
}
vd.map();
EqState(vd);
double max_visc = 0.0;
vd.ghost_get<type,rho,Pressure,velocity>();
calc_forces(vd,NN,max_visc);
double dt = calc_deltaT(vd,max_visc);
it++;
if (it < 40)
verlet_int(vd,dt);
else
{
euler_int(vd,dt);
it = 0;
}
t += dt;
if (write < t*100)
{
vd.map();
vd.ghost_get<type,rho,Pressure,velocity>();
vd.updateCellList(NN);
sensor_pressure(vd,NN,press_t,probes);
vd.write_frame("Geometry" ,write);
write++;
{std::cout <<
"TIME: " << t <<
" write " << it_time.
getwct () <<
" " << v_cl.
getProcessUnitID () <<
" " << cnt <<
" Max visc: " << max_visc << std::endl;}
}
else
{
{std::cout <<
"TIME: " << t <<
" " << it_time.
getwct () <<
" " << v_cl.
getProcessUnitID () <<
" " << cnt <<
" Max visc: " << max_visc << std::endl;}
}
}
size_t getProcessUnitID()
Get the process unit id.
Class for cpu time benchmarking.
double getwct()
Return the elapsed real time.
At the very end of the program we have always de-initialize the library
#include "Vector/vector_dist.hpp"
#include <math.h>
#include "Draw/DrawParticles.hpp"
#define BOUNDARY 0
#define FLUID 1
const double dp = 0.0085;
double h_swl = 0.0;
const double coeff_sound = 20.0;
const double gamma_ = 7.0;
const double H = 0.0147224318643;
const double Eta2 = 0.01 * H*H;
const double visco = 0.1;
double cbar = 0.0;
const double MassFluid = 0.000614125;
const double MassBound = 0.000614125;
#ifdef TEST_RUN
const double t_end = 0.001;
#else
const double t_end = 1.5;
#endif
const double gravity = 9.81;
const double rho_zero = 1000.0;
double B = 0.0;
const double CFLnumber = 0.2;
const double DtMin = 0.00001;
const double RhoMin = 700.0;
const double RhoMax = 1300.0;
double max_fluid_height = 0.0;
const size_t type = 0;
const int rho = 1;
const int rho_prev = 2;
const int Pressure = 3;
const int drho = 4;
const int force = 5;
const int velocity = 6;
const int velocity_prev = 7;
{
template <
typename Decomposition,
typename vector>
inline void addComputation(
Decomposition & dec,
vector & vd,
size_t v,
size_t p)
{
if (vd.template getProp<type>(p) == FLUID)
dec.addComputationCost(v,4);
else
dec.addComputationCost(v,3);
}
template <
typename Decomposition>
inline void applyModel(
Decomposition & dec,
size_t v)
{
dec.setSubSubDomainComputationCost(v, dec.getSubSubDomainComputationCost(v) * dec.getSubSubDomainComputationCost(v));
}
double distributionTol()
{
return 1.01;
}
};
{
while (it.isNext())
{
auto a = it.get();
double rho_a = vd.template getProp<rho>(a);
double rho_frac = rho_a / rho_zero;
vd.template getProp<Pressure>(a) = B*( rho_frac*rho_frac*rho_frac*rho_frac*rho_frac*rho_frac*rho_frac - 1.0);
++it;
}
}
const double a2 = 1.0/M_PI/H/H/H;
inline double Wab(double r)
{
r /= H;
if (r < 1.0)
return (1.0 - 3.0/2.0*r*r + 3.0/4.0*r*r*r)*a2;
else if (r < 2.0)
return (1.0/4.0*(2.0 - r)*(2.0 - r)*(2.0 - r))*a2;
else
return 0.0;
}
const double c1 = -3.0/M_PI/H/H/H/H;
const double d1 = 9.0/4.0/M_PI/H/H/H/H;
const double c2 = -3.0/4.0/M_PI/H/H/H/H;
const double a2_4 = 0.25*a2;
double W_dap = 0.0;
{
const double qq=r/H;
double qq2 = qq * qq;
double fac1 = (c1*qq + d1*qq2)/r;
double b1 = (qq < 1.0)?1.0f:0.0f;
double wqq = (2.0 - qq);
double fac2 = c2 * wqq * wqq / r;
double b2 = (qq >= 1.0 && qq < 2.0)?1.0f:0.0f;
double factor = (b1*fac1 + b2*fac2);
DW.
get (0) = factor * dx.
get (0);
DW.
get (1) = factor * dx.
get (1);
DW.
get (2) = factor * dx.
get (2);
}
inline double Tensile(double r, double rhoa, double rhob, double prs1, double prs2)
{
const double qq=r/H;
double wab;
if (r>H)
{
double wqq1=2.0f-qq;
double wqq2=wqq1*wqq1;
wab=a2_4*(wqq2*wqq1);
}
else
{
double wqq2=qq*qq;
double wqq3=wqq2*qq;
wab=a2*(1.0f-1.5f*wqq2+0.75f*wqq3);
}
double fab=wab*W_dap;
fab*=fab; fab*=fab;
const double tensilp1=(prs1/(rhoa*rhoa))*(prs1>0? 0.01: -0.2);
const double tensilp2=(prs2/(rhob*rhob))*(prs2>0? 0.01: -0.2);
return (fab*(tensilp1+tensilp2));
}
{
const double dot_rr2 = dot/(rr2+Eta2);
visc=std::max(dot_rr2,visc);
if (dot < 0)
{
const float amubar=H*dot_rr2;
const float robar=(rhoa+rhob)*0.5f;
const float pi_visc=(-visco*cbar*amubar/robar);
return pi_visc;
}
else
return 0.0;
}
template <
typename CellList>
inline void calc_forces(
particles & vd,
CellList & NN,
double & max_visc)
{
while (part.isNext())
{
auto a = part.get();
double massa = (vd.
getProp <type>(a) == FLUID)?MassFluid:MassBound;
double Pa = vd.
getProp <Pressure>(a);
vd.template getProp<force>(a)[0] = 0.0;
vd.template getProp<force>(a)[1] = 0.0;
vd.template getProp<force>(a)[2] = -gravity;
vd.template getProp<drho>(a) = 0.0;
{
auto Np = NN.getNNIteratorBox(NN.getCell(vd.
getPos (a)));
while (Np.isNext() == true )
{
auto b = Np.get();
if (a.getKey() == b) {++Np; continue ;};
double massb = (vd.
getProp <type>(b) == FLUID)?MassFluid:MassBound;
double Pb = vd.
getProp <Pressure>(b);
double r2 = norm2(dr);
if (r2 < 4.0*H*H)
{
double r = sqrt(r2);
DWab(dr,DW,r,false );
const double dot = dr.get(0)*dv.
get (0) + dr.get(1)*dv.
get (1) + dr.get(2)*dv.
get (2);
const double dot_rr2 = dot/(r2+Eta2);
max_visc=std::max(dot_rr2,max_visc);
}
++Np;
}
}
else
{
auto Np = NN.getNNIteratorBox(NN.getCell(vd.
getPos (a)));
while (Np.isNext() == true )
{
auto b = Np.get();
if (a.getKey() == b) {++Np; continue ;};
double massb = (vd.
getProp <type>(b) == FLUID)?MassFluid:MassBound;
double Pb = vd.
getProp <Pressure>(b);
double r2 = norm2(dr);
if (r2 < 4.0*H*H)
{
double r = sqrt(r2);
DWab(dr,DW,r,false );
double factor = - massb*((vd.
getProp <Pressure>(a) + vd.
getProp <Pressure>(b)) / (rhoa * rhob) + Tensile(r,rhoa,rhob,Pa,Pb) + Pi(dr,r2,v_rel,rhoa,rhob,massb,max_visc));
}
++Np;
}
}
++part;
}
}
void max_acceleration_and_velocity(
particles & vd,
double & max_acc,
double & max_vel)
{
while (part.isNext())
{
auto a = part.get();
double acc2 = norm2(acc);
double vel2 = norm2(vel);
if (vel2 >= max_vel)
max_vel = vel2;
if (acc2 >= max_acc)
max_acc = acc2;
++part;
}
max_acc = sqrt(max_acc);
max_vel = sqrt(max_vel);
}
double calc_deltaT(
particles & vd,
double ViscDtMax)
{
double Maxacc = 0.0;
double Maxvel = 0.0;
max_acceleration_and_velocity(vd,Maxacc,Maxvel);
const double dt_f = (Maxacc)?sqrt(H/Maxacc):std::numeric_limits<int>::max();
const double dt_cv = H/(std::max(cbar,Maxvel*10.) + H*ViscDtMax);
double dt=double(CFLnumber)*std::min(dt_f,dt_cv);
if (dt<double (DtMin))
dt=double(DtMin);
return dt;
}
size_t cnt = 0;
{
to_remove.clear();
double dt205 = dt*dt*0.5;
double dt2 = dt*2.0;
while (part.isNext())
{
auto a = part.get();
if (vd.template getProp<type>(a) == BOUNDARY)
{
double rhop = vd.template getProp<rho>(a);
vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[0] = 0.0;
vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[1] = 0.0;
vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[2] = 0.0;
double rhonew = vd.template getProp<rho_prev>(a) + dt2*vd.template getProp<drho>(a);
vd.template getProp<rho>(a) = (rhonew < rho_zero)?rho_zero:rhonew;
vd.template getProp<rho_prev>(a) = rhop;
++part;
continue ;
}
double dx = vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[0]*dt + vd.template getProp<force>(a)[0]*dt205;
double dy = vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[1]*dt + vd.template getProp<force>(a)[1]*dt205;
double dz = vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[2]*dt + vd.template getProp<force>(a)[2]*dt205;
double velX = vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[0];
double velY = vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[1];
double velZ = vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[2];
double rhop = vd.template getProp<rho>(a);
vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[0] = vd.template getProp<velocity_prev>(a)[0] + vd.template getProp<force>(a)[0]*dt2;
vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[1] = vd.template getProp<velocity_prev>(a)[1] + vd.template getProp<force>(a)[1]*dt2;
vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[2] = vd.template getProp<velocity_prev>(a)[2] + vd.template getProp<force>(a)[2]*dt2;
vd.template getProp<rho>(a) = vd.template getProp<rho_prev>(a) + dt2*vd.template getProp<drho>(a);
if (vd.
getPos (a)[0] < 0.000263878 || vd.
getPos (a)[1] < 0.000263878 || vd.
getPos (a)[2] < 0.000263878 ||
vd.
getPos (a)[0] > 0.000263878+1.59947 || vd.
getPos (a)[1] > 0.000263878+0.672972 || vd.
getPos (a)[2] > 0.000263878+0.903944 ||
vd.template getProp<rho>(a) < RhoMin || vd.template getProp<rho>(a) > RhoMax)
{
to_remove.add(a.getKey());
}
vd.template getProp<velocity_prev>(a)[0] = velX;
vd.template getProp<velocity_prev>(a)[1] = velY;
vd.template getProp<velocity_prev>(a)[2] = velZ;
vd.template getProp<rho_prev>(a) = rhop;
++part;
}
cnt++;
}
{
to_remove.clear();
double dt205 = dt*dt*0.5;
double dt2 = dt*2.0;
while (part.isNext())
{
auto a = part.get();
if (vd.template getProp<type>(a) == BOUNDARY)
{
double rhop = vd.template getProp<rho>(a);
vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[0] = 0.0;
vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[1] = 0.0;
vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[2] = 0.0;
double rhonew = vd.template getProp<rho>(a) + dt*vd.template getProp<drho>(a);
vd.template getProp<rho>(a) = (rhonew < rho_zero)?rho_zero:rhonew;
vd.template getProp<rho_prev>(a) = rhop;
++part;
continue ;
}
double dx = vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[0]*dt + vd.template getProp<force>(a)[0]*dt205;
double dy = vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[1]*dt + vd.template getProp<force>(a)[1]*dt205;
double dz = vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[2]*dt + vd.template getProp<force>(a)[2]*dt205;
double velX = vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[0];
double velY = vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[1];
double velZ = vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[2];
double rhop = vd.template getProp<rho>(a);
vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[0] = vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[0] + vd.template getProp<force>(a)[0]*dt;
vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[1] = vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[1] + vd.template getProp<force>(a)[1]*dt;
vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[2] = vd.template getProp<velocity>(a)[2] + vd.template getProp<force>(a)[2]*dt;
vd.template getProp<rho>(a) = vd.template getProp<rho>(a) + dt*vd.template getProp<drho>(a);
if (vd.
getPos (a)[0] < 0.000263878 || vd.
getPos (a)[1] < 0.000263878 || vd.
getPos (a)[2] < 0.000263878 ||
vd.
getPos (a)[0] > 0.000263878+1.59947 || vd.
getPos (a)[1] > 0.000263878+0.672972 || vd.
getPos (a)[2] > 0.000263878+0.903944 ||
vd.template getProp<rho>(a) < RhoMin || vd.template getProp<rho>(a) > RhoMax)
{
to_remove.add(a.getKey());
}
vd.template getProp<velocity_prev>(a)[0] = velX;
vd.template getProp<velocity_prev>(a)[1] = velY;
vd.template getProp<velocity_prev>(a)[2] = velZ;
vd.template getProp<rho_prev>(a) = rhop;
++part;
}
cnt++;
}
template <typename Vector, typename CellList>
inline void sensor_pressure(
Vector & vd,
{
press_t.add();
for (
size_t i = 0 ; i < probes.
size () ; i++)
{
float press_tmp = 0.0f;
float tot_ker = 0.0;
if (vd.getDecomposition().isLocal(probes.get(i)) == true )
{
auto itg = NN.getNNIteratorBox(NN.getCell(probes.get(i)));
while (itg.isNext())
{
auto q = itg.get();
if (vd.template getProp<type>(q) != FLUID)
{
++itg;
continue ;
}
double r = sqrt(norm2(xp - xq));
double ker = Wab(r) * (MassFluid / rho_zero);
tot_ker += ker;
press_tmp += vd.template getProp<Pressure>(q) * ker;
++itg;
}
if (tot_ker == 0.0)
press_tmp = 0.0;
else
press_tmp = 1.0 / tot_ker * press_tmp;
}
press_t.last().add(press_tmp);
}
}
int main(int argc, char * argv[])
{
openfpm_init(&argc,&argv);
probes.add({0.8779,0.3,0.02});
probes.add({0.754,0.31,0.02});
Box<3,double> domain({-0.05,-0.05,-0.05},{1.7010,0.7065,0.5025});
size_t sz[3] = {207,90,66};
W_dap = 1.0/Wab(H/1.5);
size_t bc[3]={NON_PERIODIC,NON_PERIODIC,NON_PERIODIC};
Box<3,double> fluid_box({dp/2.0,dp/2.0,dp/2.0},{0.4+dp/2.0,0.67-dp/2.0,0.3+dp/2.0});
max_fluid_height = fluid_it.getBoxMargins().
getHigh (2);
h_swl = fluid_it.getBoxMargins().
getHigh (2) - fluid_it.getBoxMargins().
getLow (2);
B = (coeff_sound)*(coeff_sound)*gravity*h_swl*rho_zero / gamma_;
cbar = coeff_sound * sqrt(gravity * h_swl);
while (fluid_it.isNext())
{
vd.add();
vd.getLastPos()[0] = fluid_it.get().get(0);
vd.getLastPos()[1] = fluid_it.get().get(1);
vd.getLastPos()[2] = fluid_it.get().get(2);
vd.template getLastProp<type>() = FLUID;
vd.template getLastProp<Pressure>() = rho_zero * gravity * (max_fluid_height - fluid_it.get().get(2));
vd.template getLastProp<rho>() = pow(vd.template getLastProp<Pressure>() / B + 1, 1.0/gamma_) * rho_zero;
vd.template getLastProp<rho_prev>() = vd.template getLastProp<rho>();
vd.template getLastProp<velocity>()[0] = 0.0;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity>()[1] = 0.0;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity>()[2] = 0.0;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity_prev>()[0] = 0.0;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity_prev>()[1] = 0.0;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity_prev>()[2] = 0.0;
++fluid_it;
}
Box<3,double> recipient1({0.0,0.0,0.0},{1.6+dp/2.0,0.67+dp/2.0,0.4+dp/2.0});
Box<3,double> recipient2({dp,dp,dp},{1.6-dp/2.0,0.67-dp/2.0,0.4+dp/2.0});
Box<3,double> obstacle1({0.9,0.24-dp/2.0,0.0},{1.02+dp/2.0,0.36,0.45+dp/2.0});
Box<3,double> obstacle2({0.9+dp,0.24+dp/2.0,0.0},{1.02-dp/2.0,0.36-dp,0.45-dp/2.0});
holes.add(recipient2);
holes.add(obstacle1);
while (bound_box.isNext())
{
vd.add();
vd.getLastPos()[0] = bound_box.get().get(0);
vd.getLastPos()[1] = bound_box.get().get(1);
vd.getLastPos()[2] = bound_box.get().get(2);
vd.template getLastProp<type>() = BOUNDARY;
vd.template getLastProp<rho>() = rho_zero;
vd.template getLastProp<rho_prev>() = rho_zero;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity>()[0] = 0.0;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity>()[1] = 0.0;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity>()[2] = 0.0;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity_prev>()[0] = 0.0;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity_prev>()[1] = 0.0;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity_prev>()[2] = 0.0;
++bound_box;
}
while (obstacle_box.isNext())
{
vd.add();
vd.getLastPos()[0] = obstacle_box.get().get(0);
vd.getLastPos()[1] = obstacle_box.get().get(1);
vd.getLastPos()[2] = obstacle_box.get().get(2);
vd.template getLastProp<type>() = BOUNDARY;
vd.template getLastProp<rho>() = rho_zero;
vd.template getLastProp<rho_prev>() = rho_zero;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity>()[0] = 0.0;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity>()[1] = 0.0;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity>()[2] = 0.0;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity_prev>()[0] = 0.0;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity_prev>()[1] = 0.0;
vd.template getLastProp<velocity_prev>()[2] = 0.0;
++obstacle_box;
}
vd.map();
vd.addComputationCosts(md);
vd.getDecomposition().decompose();
vd.map();
vd.ghost_get<type,rho,Pressure,velocity>();
auto NN = vd.getCellList(2*H);
size_t write = 0;
size_t it = 0;
size_t it_reb = 0;
double t = 0.0;
while (t <= t_end)
{
it_reb++;
if (it_reb == 200)
{
vd.map();
it_reb = 0;
vd.addComputationCosts(md);
vd.getDecomposition().decompose();
std::cout << "REBALANCED " << std::endl;
}
vd.map();
EqState(vd);
double max_visc = 0.0;
vd.ghost_get<type,rho,Pressure,velocity>();
calc_forces(vd,NN,max_visc);
double dt = calc_deltaT(vd,max_visc);
it++;
if (it < 40)
verlet_int(vd,dt);
else
{
euler_int(vd,dt);
it = 0;
}
t += dt;
if (write < t*100)
{
vd.map();
vd.ghost_get<type,rho,Pressure,velocity>();
vd.updateCellList(NN);
sensor_pressure(vd,NN,press_t,probes);
vd.write_frame("Geometry" ,write);
write++;
{std::cout <<
"TIME: " << t <<
" write " << it_time.
getwct () <<
" " << v_cl.
getProcessUnitID () <<
" " << cnt <<
" Max visc: " << max_visc << std::endl;}
}
else
{
{std::cout <<
"TIME: " << t <<
" " << it_time.
getwct () <<
" " << v_cl.
getProcessUnitID () <<
" " << cnt <<
" Max visc: " << max_visc << std::endl;}
}
}
openfpm_finalize();
}